Python projects documentation
- applications/prometheus-alert-zendesk.
- core-service-lib.
- reporting/data-service.
- reporting/rbac-service.
- reporting/scheduler-service.
- vanilla-project.
Python Best Practices
Python is an interpreted language and not compiled, this mean most of the errors will occured at the runtime. To avoid this, you must take all advantages to reduce this risk.
Dependencies
Never develop directly on your computer, use dockerized environment to ensure reproductivity and stability. Working on 2 projects requiring different Python version will cause dependency nightmare. Dockerized environment will isolate project and their dependencies into a controlled space.
Code formatting
# Sort imports
isort <dir>
# Format
black <dir>
Code review
- Focus on logic
- Don't look at formatting, run tools
Typing
Python is a lazy language, variables, functions will accept any type objects without warnings and this could errors at runtime. To prevent runtime error, take advantage of your IDE by typing arguments and returned object to get highlighted problems.
Example:
def funct(argument1: str, argument2: bool) -> str:
...
return "a_string"
IDE will show problems if wrong object type are passed to the function or returned by the function.
- https://sunscrapers.com/blog/python-best-practices-static-typing-in-python-with-mypy/
- https://realpython.com/python-type-checking/#static-typing
Documentation
Documenting classes, functions is nice but will always be out of sync with the real code or will take consume time of code review without real gain.
Prerequisites
Docker
Go to the settings of your laptop : "System Preference" -> "Security and Privacy" -> "Privacy". Select "Files and Folders" and check every box under "Docker".
Visual Studio Code
In Visual Studio Code, install plugin "Dev Containers" : https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode-remote.remote-containers
Starting new project
- Create a gitlab project e.g. Wonderful-project
- Clone vanilla-project
git clone git@gitlab.thalesdigital.io:platform-team-canada/k8saas-private/vanilla-project.git - Clone Wonderful-project
cd Wonderful-project- Select a free port and update this documentation [Section Running multiple devcontainer simultaneous]
- run script
../vanilla-project/createProject.sh -p <wonderful-vscode-container-port> - commit changes
git add .
git add -f .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server-insiders/.notempty
git add -f .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server/.notempty
git commit -m "Added project shell from vanilla project"
git push - gitlab
- Activate shared runners
- Activate coverage parsing
- Gitlab 15.0+
- Gitlab 15.0-
-
Edit project ```.gitlab-ci.yml"
-
Add
coverage: '/(?i)total.*? (100(?:\.0+)?\%|[1-9]?\d(?:\.\d+)?\%)$/'as show below[...]
test-python:
stage: test
coverage: '/(?i)total.*? (100(?:\.0+)?\%|[1-9]?\d(?:\.\d+)?\%)$/'
image:
[...]
Configure code coverage in gitlab: -> Project settings -> CI/CD -> General piplines -> Test coverage parsing -> set: ^TOTAL.+?(\d+\%)$
Development
testing entry points
Inside development environment (vscode)
-
Tests On the side toolbar, select Testing (lab becher icon), you should see the project tests otherwise, click on the refresh icon. You can run all or a selection of tests from this panel. There is also the possibility of running these tests in debug mode by using the betttle icon instead of play.
-
Calling main inside terminal (command line) In a terminal where venv is activated, the main function can be run
python -m vanilla_project.vanillaprojectormake runm -
Running the current opened file in vscode On left, use the play icon with bug -> select Python current file then play.
-
Live testing
- Watch all tests on save
Open a terminal window and run
make watcha - Watch all tests in a file on save
Note: Add
@currentat the top of the test feature file(s) you are currently working on (but do not commit it). On every save it will execute all the@currenttests, if they are successful it will then execute all the unit tests, run flake and pylint. Open a terminal window and runmake watchc
Integration tests
By default integration tests are visible in vscode but they are ignored when Run All Tests is executed.
Integration tests can be run one at a time in vscode (one test, not one class).
To run all the integration tests from the console: pytest -s -m integration
To run (and debug in vscode) all integration tests, select the launch configuration Python: Run all integration tests
To run (and debug in vscode) a single integration test class, open in and select the launch configuration Python: Test current file
Using debbuger
The debugger can be run from 2 different area
- Single or multiple tests: the vscode Testing panel
- Current file from its main function: Click on the Run menu at the top -> Start Debugging -> Python File (current file)
Outside development environment (vscode)
Docker
This project contains 2 scripts to help building and running the project inside docker container.
dockerBuild.shis a tool to create docker image including building the python wheel if wanted. When the script is launched, the question vscode container is running, rebuild the project? [yN] if and only if the vscode container is running.- Answering Y will build the whl package before building the docker image. This case is useful when the code has been modified since the last whl package build.
- Answering N will using the existing whl package for building the docker image. This case is useful when the code has not been modified since the last whl package build and you want to troubleshoot the docker image content.
- If the vscode container is not running, the existing whl package will be used without the possibility of re-building it because building the whl package requires the developement inside vscode.
dockerRun.shis a tool a run the docker container for the docker image built from the previous step. Note that this script is highly dependant of your application in terms of volumes to be mounted, execution name and path, arguments, ...
Helm
The helm is the way to deploy the service in a k8s cluster. The helm will use the tag latest to get the docker image from the gitlab docker registery. It is also possible to change the tag value inside helm/values.yaml to use another tag. e.g. <branch-name>-latest
# install
helm install vanilla-project helm -n k8saas-microservices
# uninstall
helm uninstall vanilla-project -n k8saas-microservices
HTTP status code
4XX Client errors
400 Bad Request
The server could not understand the request due to invalid syntax.
401 Unauthorized
Although the HTTP standard specifies "unauthorized", semantically this response means "unauthenticated". That is, the client must authenticate itself to get the requested response.
403 Forbidden
The client does not have access rights to the content; that is, it is unauthorized, so the server is refusing to give the requested resource. Unlike 401, the client's identity is known to the server.
404 Not Found
The server can not find the requested resource. In the browser, this means the URL is not recognized. In an API, this can also mean that the endpoint is valid but the resource itself does not exist. Servers may also send this response instead of 403 to hide the existence of a resource from an unauthorized client. This response code is probably the most famous one due to its frequent occurrence on the web.
5XX Server errors
500 Internal Server Error
The server has encountered a situation it doesn't know how to handle.
501 Not Implemented
The request method is not supported by the server and cannot be handled. The only methods that servers are required to support (and therefore that must not return this code) are GET and HEAD.
502 Bad Gateway
This error response means that the server, while working as a gateway to get a response needed to handle the request, got an invalid response.
503 Service Unavailable
The server is not ready to handle the request. Common causes are a server that is down for maintenance or that is overloaded. Note that together with this response, a user-friendly page explaining the problem should be sent. This responses should be used for temporary conditions and the Retry-After: HTTP header should, if possible, contain the estimated time before the recovery of the service. The webmaster must also take care about the caching-related headers that are sent along with this response, as these temporary condition responses should usually not be cached.
Releasing python procedure
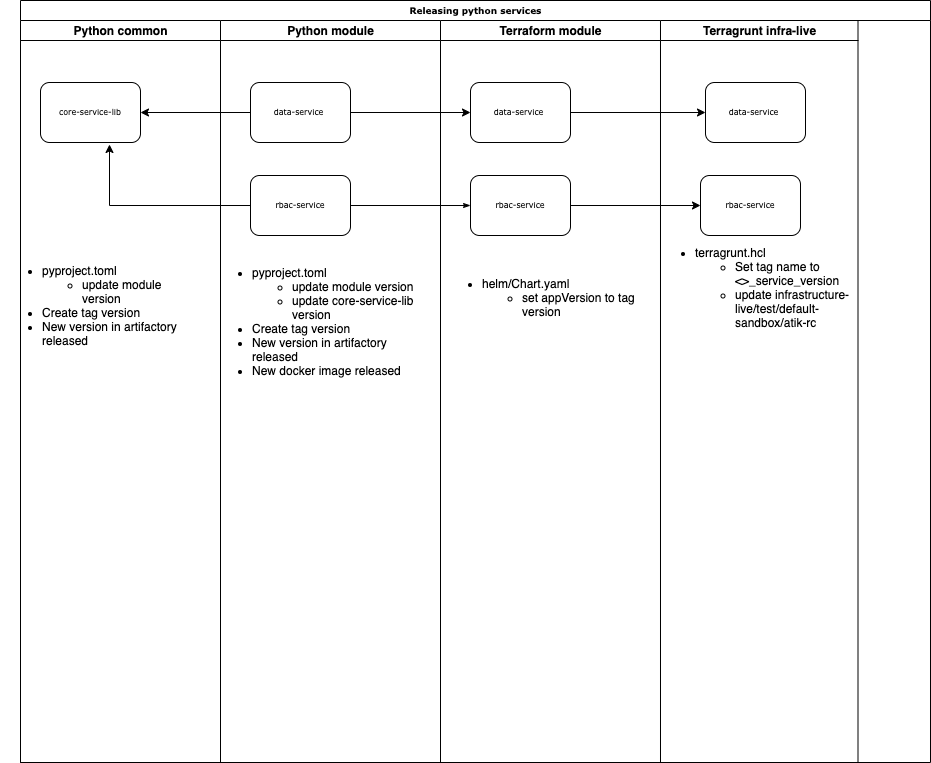
Versionning
Python versionning scheme is very strict about how packages are named
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0440/
The canonical public version identifiers MUST comply with the following scheme:
[N!]N(.N)*[{a|b|rc}N][.postN][.devN]
This forced pattern doesn't allow to include the following development concept in the package name.
- branch name
- commit sha
Notes: There is something broken with rc.dev pattern. Poetry doesn't get the newer release of the package. The rc idea for the master branch will be removed.
In project being built
To conform with pip, pipenv and our git flow, we need version numbers of the form:
- tag, releases:
Major.minor.revision(M.m.R) - master, stable:
M.m.R.devN- where N is the pipeline ID (any length integer)
- Example: 1.2.0rc.dev123456
- Not tested yet feature branch, task, spike:
M.m.RaBBBB.devN- where BBBB is the feature number (Jira US ID, integer only), and N is the pipeline ID
- Example: 1.2.0a526.dev123456
Note that there is not dot before a or rc and rc is equivalent to rc0 or a and a0
The .devN part is added by a CI tool such as Gitlab, and N be automatically incremented on each build, whether or not it is successful (but only successful builds get pushed on the Artifactory).
As such, developers should only put the part before .devN.
Requiring a project by version
A project that would use a library with the above version scheme would specify, in its requirement strings:
- tag:
"M.m.r"- pinned to a specific version
- master:
"^M.m.r.dev0"- i.e. any 'master' version before the next release, but no feature branch
- Not tested yet feature branch:
"^M.m.RaBBBB.devN,- i.e. any version in the branch BBBB
In practice
- On tag"
- Dev will create a tag named
M.m.Rfrom master whereM.m.Ris the version inside file pyproject.toml - CI will release a version
M.m.R - Dev will upgrade version in master to the next release candidate
M.(m+1).R
- Dev will create a tag named
- master:
- CI will release a version
M.m.R.dev<pipeline#>
- CI will release a version
- feature branch:
- Dev will set version to the US#
poetry version M.m.Ra<US#> - CI will release a version
M.m.Ra<US#>.dev<pipeline#>
- Dev will set version to the US#
CI/CD
Build sequence
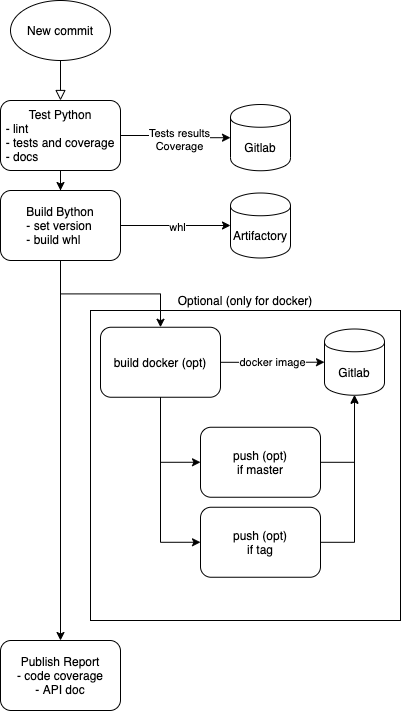
Configure code coverage in gitlab UI
-> Project settings -> CI/CD -> General piplines -> Test coverage parsing
set: ^TOTAL.+?(\d+\%)$
Troubleshooting development environment
Attrbute Error, README.md is not a package
Error:
ValueError
README.md is not a package.
For undetermined reason, some file at project root are causing issue with poetry. This comes from *.md inclusion in the pyproject.toml file in packages section. To fix this issue, comment the line { include = "*.md", format = "sdist" }, as shown below.
packages = [
{ include = "billing_api" },
# { include = "*.md", format = "sdist" },
# This will not include the generated documentation as it is in the .gitignore file
# { include = "docs", format = "sdist" },
]
Running poetry install with option --no-root will also work
https://github.com/python-poetry/poetry-core/pull/123
Running multiple devcontainer simultaneous
Each container must use a different port. Change port to use into .devcontainer/docker-compose.yml
Reservation List sorted by port number.
| Component | Dev port |
|---|---|
| reporting/scheduler | 9011 |
| reporting/data | 9012 |
| coreservice | 9013 |
| reporting/rbac | 9014 |
| vanilla | 9015 |
| applications/prometheus-alert-zendesk | 9016 |
| reporting/reporting-service | 9017 |
| keda-prometheus-app | 9018 |
| prometheus-alert-postit | 9019 |
| git-utility | 9020 |
| k8saasctl | 9021 |
| billing-api | 9101 |
| test-automation | 9102 |
| metadata-api | 9201 |
| documentation-chatbot-api | 9202 |
Cannot start service vscode-container: ... port is already allocated
Each project running into vscode needs their unique port to be run simultaneously. Edit .devcontainer/docker-compose and change the forwarded port to a free port.
Cannot open dev container in vscode
- Logs error:
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/home/vscode/.vscode-server/bin’: Permission denied
mkdir: cannot create directory ‘/home/vscode/.vscode-server/data’: Permission denied
- Missing folders in your project Folders .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server and devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server-insiders were not part of your cloned project and these folders have been created by docker with root onwership
- Change folder ownership
# Inside your project clone
sudo chown -R $(whoami): .
- Add missing folder to your project
# At root of your project clone
mkdir -p .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server-insiders
mkdir -p .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server
touch .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server-insiders/.notempty
touch .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server/.notempty
git add -f .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server-insiders/.notempty
git add -f .devcontainer/volumes/vscode-server/.notempty
git add .; git commit -m "Added empty folder to prevent creation by root";git push
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '...'
When run with command line, toml script or vscode play tab, ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '...' means that your project has not been installed or not up-to-date in venv content. Run poetry install and re-try
SSH agent is not running or no keys are available
Solution: start ssh agent in a terminal ssh-add. This will load your local ssh keys.
No testing icon on the side toolbar
Note: if .vscode-server directory is not empty, extensions are not installed even if they aren't.
Option 1
Information: Python Test Log console output
python /home/vscode/.vscode-server/extensions/ms-python.python-2021.5.842923320/pythonFiles/testing_tools/run_adapter.py discover pytest -- --rootdir /workspace -s --cache-clear
Error: spawn <python executable> ENOENT
Solution:
- Missing .vscode folder at project root
poetry shellpoetry install --remove-untracked
Option 2
Install Python vscode extension
Poetry install error with 'Link' object has no attribute 'is_absolute'
Error messages:
• Installing urllib3 (1.26.7): Failed
AttributeError
'Link' object has no attribute 'is_absolute'
at /usr/local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/poetry/core/packages/file_dependency.py:33 in __init__
29│ self._path = path
30│ self._base = base or Path.cwd()
31│ self._full_path = path
32│
→ 33│ if not self._path.is_absolute():
34│ try:
35│ self._full_path = self._base.joinpath(self._path).resolve()
36│ except FileNotFoundError:
37│ raise ValueError("Directory {} does not exist".format(self._path))
Solution: rebuild you docker container.
Gitlab-ci
CICD variables
- ARTIFACTORY_API_KEY
- ARTIFACTORY_USERNAME
Artifactory
Client configuration location
- Repo list: ~/.config/pypoetry/config.toml
- Repo usernames: ~/.config/pypoetry/auth.toml
- Repo passwords: ~/.local/share/python_keyring/sagecipher_pass.cfg
- Pip repo: ~/.pip/pip.conf
Hints
poetry verbose:
-v, -vv, -vvv
Example: poetry install -vvv
Removed installed lib
NOTE: The lib will be removed from the toml file.
poetry remove <lib>
poetry install --remove-untracked failed
Inside dev environment, rm -rf /workspace/.venv/*